8.8
Excellent
Elliptical Trainer Images
Elliptical Trainer Instructions
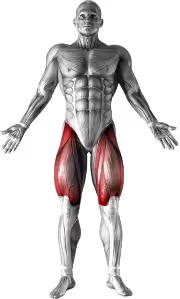
- To begin, step onto the elliptical and select the desired option from the menu. Most ellipticals have a manual setting, or you can select a program to run. Typically, you can enter your age and weight to estimate the amount of calories burned during exercise. Elevation can be adjusted to change the intensity of the workout.
- The handles can be used to monitor your heart rate to help you stay at an appropriate intensity.
Ellipticals offer convenience, cardiovascular benefits, and have far less impact on joints than ground-based cardio such as running. A 150 lb person will burn on average 387 calories in 30 minutes, compared to more than 450-700 calories running. It’s recommended that you use the arms on the elliptical to create more movement, if your elliptical has them.
8.7
Excellent
Dumbbell Rear Lunge Images
Dumbbell Rear Lunge Instructions

- Stand with your torso upright holding two dumbbells in your hands by your sides. This will be your starting position.
- Step backward with your right leg around two feet or so from the left foot and lower your upper body down, while keeping the torso upright and maintaining balance. Inhale as you go down. Tip: As in the other exercises, do not allow your knee to go forward beyond your toes as you come down, as this will put undue stress on the knee joint. Make sure that you keep your front shin perpendicular to the ground. Keep the torso upright during the lunge; flexible hip flexors are important. A long lunge emphasizes the Gluteus Maximus; a short lunge emphasizes Quadriceps.
- Push up and go back to the starting position as you exhale. Tip: Use the ball of your feet to push in order to accentuate the quadriceps. To focus on the glutes, press with your heels.
- Now repeat with the opposite leg.
9.5
Excellent
Clean from Blocks Images
Clean from Blocks Instructions

-
- With a barbell on boxes or stands of the desired height, take an overhand or hook grip just outside the legs. Lower your hips with the weight focused on the heels, back straight, head facing forward, chest up, with your shoulders just in front of the bar. This will be your starting position.
- Begin the first pull by driving through the heels, extending your knees. Your back angle should stay the same, and your arms should remain straight with the elbows pointed out.
Next comes the second pull, the main source of acceleration for the clean. As the bar approaches the mid-thigh position, begin extending through the hips. In a jumping motion, accelerate by extending the hips, knees, and ankles, using speed to move the bar upward. There should be no need to actively pull through the arms to accelerate the weight. At the end of the second pull, the body should be fully extended, leaning slightly back, with the arms still extended.
- As full extension is achieved, transition into the receiving position by aggressively shrugging and flexing the arms with the elbows up and out. Aggressively pull yourself down, rotating your elbows under the bar as you do so. Receive the bar in a front squat position, the depth of which is dependent upon the height of the bar at the end of the third pull. The bar should be racked onto the protracted shoulders, lightly touching the throat with the hands relaxed. Continue to descend to the bottom squat position, which will help in the recovery.
- Immediately recover by driving through the heels, keeping the torso upright and elbows up. Continue until you have risen to a standing position. Return the weight to the boxes for the next rep.
8.8
Excellent
Burpee Images
Burpee Instructions

- Begin standing with your legs shoulder-width apart.
- Place your hands on the floor and kick your legs back so you end up with your stomach and thighs on the floor. Your elbows should be bent.
- From this position, press up like you’re doing a push-up and push your hips up.
- Jump your feet under your hips and stand.
- Finish the movement by jumping in the air and bringing your hands over your head.
- Repeat.
9.3
Excellent
Box Squat Images
Box Squat Instructions

- The box squat allows you to squat to desired depth and develop explosive strength in the squat movement. Begin in a power rack with a box at the appropriate height behind you. Typically, you would aim for a box height that brings you to a parallel squat, but you can train higher or lower if desired.
- Begin by stepping under the bar and placing it across the back of the shoulders. Squeeze your shoulder blades together and rotate your elbows forward, attempting to bend the bar across your shoulders. Remove the bar from the rack, creating a tight arch in your lower back, and step back into position. Place your feet wider for more emphasis on the back, glutes, adductors, and hamstrings, or closer together for more quad development. Keep your head facing forward.
- With your back, shoulders, and core tight, push your knees and butt out and you begin your descent. Sit back with your hips until you are seated on the box. Ideally, your shins should be perpendicular to the ground. Pause when you reach the box, and relax the hip flexors. Never bounce off of a box.
- Keeping the weight on your heels and pushing your feet and knees out, drive upward off of the box as you lead the movement with your head. Continue upward, maintaining tightness head to toe.
8.8
Excellent
Barbell Lunge Images
Barbell Lunge Instructions

- This exercise is best performed inside a squat rack for safety purposes. To begin, first set the bar on a rack just below shoulder level. Once the correct height is chosen and the bar is loaded, step under the bar and place the back of your shoulders (slightly below the neck) across it.
- Hold on to the bar using both arms at each side and lift it off the rack by first pushing with your legs and at the same time straightening your torso.
- Step away from the rack and step forward with your right leg and squat down through your hips, while keeping the torso upright and maintaining balance. Inhale as you go down. Note: Do not allow your knee to go forward beyond your toes as you come down, as this will put undue stress on the knee joint.
- Using mainly the heel of your foot, push up and go back to the starting position as you exhale.
- Repeat the movement for the recommended amount of repetitions and then perform with the left leg.
9.4
Excellent
Barbell Full Squat Images
Barbell Full Squat Instructions

- This exercise is best performed inside a squat rack for safety purposes. To begin, first set the bar on a rack just above shoulder level. Once the correct height is chosen and the bar is loaded, step under the bar and place the back of your shoulders (slightly below the neck) across it.
- Hold on to the bar using both arms at each side and lift it off the rack by first pushing with your legs and at the same time straightening your torso.
- Step away from the rack and position your legs using a shoulder-width medium stance with the toes slightly pointed out. Keep your head up at all times and maintain a straight back. This will be your starting position.
- Begin to slowly lower the bar by bending the knees and sitting back with your hips as you maintain a straight posture with the head up. Continue down until your hamstrings are on your calves. Inhale as you perform this portion of the movement.
- Begin to raise the bar as you exhale by pushing the floor with the heel or middle of your foot as you straighten the legs and extend the hips to go back to the starting position.
- Repeat for the recommended amount of repetitions.
This type of squat allows a greater range of motion, and allows the trunk to maintain a more vertical position than other types of squats, due to foot position and the higher bar position.
7
Good
Pin Presses Images
Pin Presses Instructions
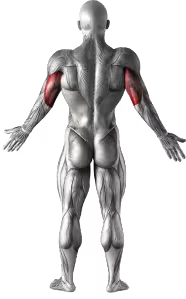
- Pin presses remove the eccentric phase of the bench press, developing starting strength. They also allow you to train a desired range of motion.
- The bench should be set up in a power rack. Set the pins to the desired point in your range of motion, whether it just be lockout or an inch off of your chest. The bar should be moved to the pins and prepared for lifting.
- Begin by lying on the bench, with the bar directly above the contact point during your regular bench. Tuck your feet underneath you and arch your back. Using the bar to help support your weight, lift your shoulder off the bench and retract them, squeezing the shoulder blades together. Use your feet to drive your traps into the bench. Maintain this tight body position throughout the movement.
- You can take a standard bench grip, or shoulder width to focus on the triceps. The bar, wrist, and elbow should stay in line at all times. Focus on squeezing the bar and trying to pull it apart.
- Drive the bar up with as much force as possible. The elbows should be tucked in until lockout.
- Return the bar to the pins, pausing before beginning the next repetition.
Close-Grip%20Push-Up%20off%20of%20a%20Dumbbell
7.3
Good
Close-Grip Push-Up off of a Dumbbell Images
Close-Grip Push-Up off of a Dumbbell Instructions

- Lie on the floor and place your hands on an upright dumbbell. Supporting your weight on your toes and hands, keep your torso rigid and your elbows in with your arms straight. This will be your starting position.
- Lower your body, allowing the elbows to flex while you inhale. Keep your body straight, not allowing your hips to rise or sag.
- Press yourself back up to the starting position by extending the elbows. Breathe out as you perform this step.
- After a pause at the contracted position, repeat the movement for the prescribed amount of repetitions.
The Tate Press is an excellent triceps exercise that targets the long head of the triceps, which is often difficult to engage with other pressing movements. By performing this exercise on a bench with your arms in a specific position, the Tate Press isolates the triceps more effectively, promoting strength and muscle growth. Incorporating Tate Press into your routine can help build stronger, more defined triceps, and is especially beneficial for individuals looking to enhance their arm strength.
Tate Press Video
How to Perform Tate Press
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up the Bench: Position a flat bench and lie on your back with your feet flat on the floor. Grip the dumbbells with your palms facing inward, keeping your elbows bent and out to the sides.
- Choose the Right Weight: Pick a weight that challenges your triceps while maintaining control. Begin with a moderate weight to ensure proper form.
- Grip the Dumbbells: Hold the dumbbells with a neutral grip, keeping your elbows at a 45-degree angle from your body.
- Lower the Dumbbells: Slowly lower the dumbbells towards your chest while keeping your upper arms stationary. Focus on feeling the stretch in your triceps.
- Press the Dumbbells Back Up: Push the dumbbells back to the starting position, fully extending your arms without locking your elbows.
- Complete the Reps: Repeat the movement for the desired number of reps, maintaining control and proper form.
Tate Press Benefits
- Targeted Triceps Development: The Tate Press specifically targets the long head of the triceps, improving the muscle’s overall strength and appearance.
- Improved Arm Definition: This movement helps build more defined arms by focusing on the triceps, a key muscle for achieving a sculpted look.
- Increased Strength: The Tate Press helps increase triceps strength, which is beneficial for pressing movements like bench press and overhead press.
- Better Elbow Health: The exercise helps strengthen the elbow joint and surrounding muscles, improving overall upper-body performance.
- Versatile Exercise: Tate Press can be performed with dumbbells, making it an adaptable exercise for home or gym workouts.
Tate Press Muscles Worked
The Tate Press primarily targets the triceps, specifically the long head of the triceps brachii. The forearm muscles are also engaged during the movement to stabilize the dumbbells, and the deltoids contribute slightly during the press phase.



































