The Ab Roller is a popular core exercise designed to engage the entire abdominal region, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis. This exercise utilizes a rolling motion that challenges stability, helps build strength, and tones the abdominal muscles. The Ab Roller is an effective way to enhance muscle endurance and core stability, making it a go-to for individuals looking to improve overall core strength and achieve a toned midsection.
Ab Roller Video
How to Perform Ab Roller
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up the Ab Roller: Kneel on the floor and place your hands on the handles of the Ab Roller. Ensure your wrists are aligned with your shoulders.
- Engage Your Core: Tighten your abdominal muscles to stabilize your body. Keep your back straight and avoid sagging.
- Roll Forward: Slowly roll the Ab Roller forward, extending your body while maintaining core engagement. Go as far as you can without allowing your lower back to arch excessively.
- Return to Starting Position: Reverse the motion by pulling the Ab Roller back towards your knees, maintaining core tension throughout the movement.
- Breathing: Exhale as you roll the Ab Roller forward and inhale as you return to the starting position.
- Control the Movement: Avoid rushing the movement. Focus on controlled, deliberate motions to ensure maximum activation of the abdominal muscles.
Ab Roller Benefits
- Strengthens Core Muscles: The Ab Roller is one of the most effective exercises for engaging and strengthening the entire core, including the abdominals, lower back, and hips.
- Improves Stability and Balance: The dynamic movement of the Ab Roller enhances your balance, stability, and coordination, improving overall athletic performance.
- Increases Endurance: By targeting the core with controlled, high-repetition movements, the Ab Roller helps build muscular endurance in the abdominal muscles.
- Reduces Lower Back Pain: Strengthening the core with the Ab Roller helps stabilize the spine and reduces the risk of lower back pain.
- Enhances Muscle Definition: Regular use of the Ab Roller contributes to muscle toning, particularly in the abdominal region, resulting in a leaner, more defined appearance.
Ab Roller Muscles Worked
The Ab Roller primarily targets the following muscles:
- Rectus Abdominis: The primary muscle worked during the Ab Roller, responsible for the “six-pack” appearance.
- Obliques: These muscles along the sides of the abdomen are also engaged, especially during the forward rolling movement.
- Transverse Abdominis: This deep abdominal muscle is activated to stabilize the trunk and maintain posture during the exercise.
- Hip Flexors: These muscles help control the movement and assist in stabilizing the body during the rolling motion.
- Lower Back: Although not the primary target, the lower back muscles are engaged to stabilize the spine during the exercise.
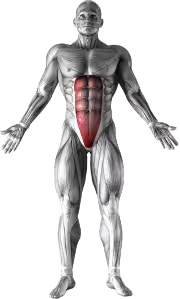
Related Exercises
The Barbell Thruster is a powerful, full-body exercise that combines a front squat and an overhead press in a single movement. This dynamic exercise targets multiple muscle groups, including the quads, glutes, shoulders, and triceps. The Barbell Thruster is a high-intensity movement often included in CrossFit workouts due to its ability to improve strength, power, and cardiovascular endurance. It engages both the lower and upper body in a functional pattern, making it an effective movement for overall fitness.
Barbell Thruster Video
How to Perform Barbell Thruster
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up the Barbell: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, and place a barbell across the front of your shoulders. Grip the barbell with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width, keeping your elbows high.
- Lower Into a Squat: Push your hips back and bend your knees, lowering your body into a squat position. Keep your chest up and your back straight as you descend.
- Explosive Drive: Drive through your heels to push your body back up to the standing position. As you rise, use the momentum to press the barbell overhead.
- Overhead Press: Extend your arms fully at the top, locking your elbows and shoulders to press the barbell overhead. Your core should remain engaged throughout the movement.
- Lower the Barbell: Reverse the movement by bringing the barbell back down to the front rack position, then immediately descend back into the next squat.
Barbell Thruster Benefits
- Full-Body Activation: The Barbell Thruster recruits multiple muscle groups, including the legs, glutes, shoulders, and triceps, offering a complete workout in one movement.
- Improves Strength and Power: By combining squats with an overhead press, this exercise builds strength and power in the lower and upper body.
- Enhances Cardiovascular Endurance: Due to its dynamic, high-intensity nature, the Barbell Thruster is great for improving cardiovascular endurance and overall conditioning.
- Increases Functional Strength: The Barbell Thruster mimics real-life movements, making it beneficial for functional fitness and everyday strength.
- Time-Efficient Workout: The Barbell Thruster is an efficient exercise that targets multiple muscle groups, allowing you to achieve a full-body workout in a short period of time.
Barbell Thruster Muscles Worked
The Barbell Thruster primarily targets the following muscles:
- Quads: The quadriceps are heavily engaged during the squat portion of the movement to extend the knees and propel the body upward.
- Glutes: The glute muscles help drive the hips upward during the explosive squat and are engaged during the overhead press.
- Shoulders (Deltoids): The deltoid muscles are activated during the overhead press as you extend your arms to lift the barbell.
- Triceps: The triceps assist in locking out the elbows during the overhead press phase of the movement.
- Core: The core muscles (rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis) are crucial for stabilizing the body throughout the entire movement.
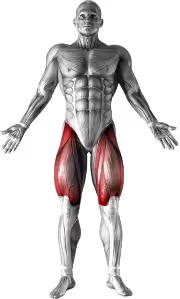
Related Exercises
The Suspended Curl is a variation of the traditional bicep curl that adds an element of instability, which forces the muscles to work harder to stabilize the body. This exercise is performed using a suspension trainer, such as TRX, which helps engage more muscle fibers in the arms, core, and shoulders. The Suspended Curl is excellent for targeting the biceps while also improving balance, coordination, and core strength. By incorporating this exercise into your routine, you can increase the effectiveness of your biceps training and enhance overall body control.
Suspended Curl Video
How to Perform Suspended Curl
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up the Suspension Trainer: Attach the suspension trainer to a stable overhead structure. Adjust the straps so that they are at about chest height when you’re standing.
- Position Yourself: Stand facing the suspension trainer, holding the handles with both hands. Step back to create tension in the straps. Lean back slightly while keeping your body straight from head to heels.
- Perform the Curl: Curl your hands toward your face, engaging your biceps while maintaining a stable body position. Keep your elbows close to your sides throughout the movement.
- Controlled Return: Slowly extend your arms back to the starting position, controlling the movement as you return to the initial position. Maintain tension in the straps throughout the exercise.
- Repeat: Perform the desired number of repetitions while focusing on proper form and controlled movement.
Suspended Curl Benefits
- Increased Bicep Activation: The instability of the suspension trainer forces the biceps to work harder during the curl, resulting in greater muscle engagement.
- Core Engagement: Your core must remain engaged to stabilize your body throughout the movement, which helps to strengthen your abs and lower back.
- Improved Balance and Coordination: The suspended nature of the exercise challenges your balance and coordination, enhancing your overall functional fitness.
- Enhanced Flexibility: The range of motion in the Suspended Curl can help improve your flexibility and mobility in the arms and shoulders.
- Time Efficiency: The Suspended Curl is a compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, allowing you to get a full-body workout in less time.
Suspended Curl Muscles Worked
The Suspended Curl primarily targets the following muscles:
- Biceps: The primary muscle worked during this exercise, the biceps are heavily engaged to perform the curl and lift the body upward.
- Forearms: The forearms assist in gripping the suspension trainer handles and stabilizing the movement.
- Core: The abdominal and lower back muscles engage to maintain stability throughout the exercise, helping to prevent the body from swaying or falling.
- Shoulders: The shoulders act as stabilizers to support the body during the movement, particularly in the extended position at the start and end of the curl.

Related Exercises
The Overhead Cable Curl is a variation of the traditional bicep curl performed on a cable machine with the cables positioned overhead. This unique setup allows for a greater stretch of the biceps at the bottom of the movement, providing a more effective muscle engagement throughout the curl. The overhead angle of the exercise helps emphasize the long head of the biceps, resulting in improved arm development and a more complete bicep workout. Incorporating the Overhead Cable Curl into your routine can help increase muscle growth, strength, and definition in the biceps.
Overhead Cable Curl Video
How to Perform Overhead Cable Curl
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up the Cable Machine: Attach a rope handle to the low pulley on a cable machine. Adjust the height so that the cables are positioned overhead when standing.
- Position Yourself: Stand facing away from the machine, gripping the rope handles with your palms facing up. Step forward to create tension in the cables, and then tilt your torso slightly forward while keeping your core tight and body straight.
- Perform the Curl: Curl the rope handles toward your forehead, engaging your biceps as you bring the handles upward. Keep your elbows stationary and close to your head during the movement.
- Controlled Return: Slowly lower the rope handles back to the starting position, keeping tension in the cables and maintaining control throughout the movement.
- Repeat: Perform the desired number of repetitions, focusing on proper form and controlled movements throughout the set.
Overhead Cable Curl Benefits
- Targeted Bicep Activation: The overhead position of the cable helps target the long head of the biceps, improving arm definition and strength.
- Increased Range of Motion: The angle of the movement allows for a greater stretch at the bottom of the curl, leading to a more effective muscle contraction.
- Constant Tension: The cable machine provides continuous tension throughout the entire range of motion, increasing muscle engagement during the curl.
- Improved Arm Development: By incorporating the Overhead Cable Curl into your workout, you can create a more balanced and defined bicep shape.
- Variety in Training: This exercise adds variety to your arm training, offering a unique angle that works the biceps differently than traditional curls.
Overhead Cable Curl Muscles Worked
The Overhead Cable Curl primarily targets the following muscles:
- Biceps: The primary muscle worked during this exercise, the biceps are heavily engaged to perform the curl and lift the weight.
- Forearms: The forearms help to grip the rope handles and maintain tension throughout the curl.
- Shoulders: The shoulders assist in stabilizing the arms during the movement, particularly when the arms are raised overhead.
- Core: The core stabilizes the body throughout the exercise, maintaining proper posture and balance during the curl.

Related Exercises
The Dumbbell Clean is a versatile and dynamic exercise that targets multiple muscle groups, focusing on strength, coordination, and power. It involves lifting dumbbells from the ground to shoulder level in one fluid motion. This movement is excellent for building full-body strength, improving athletic performance, and enhancing explosive power. The Dumbbell Clean can be a great addition to any functional fitness or strength training routine.
Dumbbell Clean Video
How to Perform Dumbbell Cleans
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up Your Dumbbells: Place the dumbbells on the floor in front of you. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, keeping your back straight.
- Grip the Dumbbells: Bend at your hips and knees to grasp the dumbbells with a neutral grip, palms facing each other.
- Initiate the Lift: Drive through your heels and extend your hips and knees, lifting the dumbbells off the ground.
- Pull and Shrug: As the dumbbells pass your knees, explosively pull them upwards and shrug your shoulders to generate momentum.
- Catch the Dumbbells: Rotate your wrists and elbows under the dumbbells, catching them at shoulder height in a standing position.
- Return to Start: Lower the dumbbells back to the ground in a controlled manner, maintaining good form. Repeat for the desired number of reps.
Dumbbell Clean Benefits
- Full-Body Strength: The Dumbbell Clean targets the lower body, upper body, and core, making it a comprehensive strength-building exercise.
- Improved Coordination: The dynamic nature of the movement enhances motor control and coordination.
- Explosive Power: This exercise develops explosive power and speed, which are crucial for athletic performance.
- Enhanced Grip Strength: Holding and lifting the dumbbells improves grip strength and forearm endurance.
- Versatility: The Dumbbell Clean can be modified for different fitness levels and training goals.
Dumbbell Clean Muscles Worked
The Dumbbell Clean is a full-body exercise that primarily targets the glutes, hamstrings, quadriceps, and deltoids. Secondary muscles involved include the trapezius, biceps, core, and forearm muscles, making it a well-rounded movement for overall strength and power development.
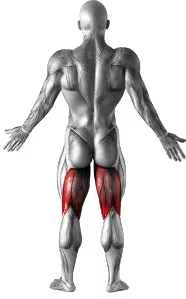
Related Exercises
The Romanian Deadlift is a powerful exercise that targets the posterior chain, including the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. This movement is an essential addition to any strength training program, improving flexibility, stability, and strength in the lower body. By maintaining a controlled motion, the Romanian Deadlift effectively isolates the target muscles while minimizing strain on the lower back.
Romanian Deadlift Video
How to Perform Romanian Deadlifts
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and hold a barbell or dumbbells with an overhand grip in front of your thighs.
- Engage Your Core: Brace your core and maintain a slight bend in your knees throughout the exercise.
- Lower the Weight: Hinge at your hips to lower the weight, keeping your back flat and your head neutral.
- Feel the Stretch: Descend until you feel a stretch in your hamstrings, ensuring the barbell stays close to your legs.
- Return to Start: Drive through your heels and extend your hips to return to the starting position, squeezing your glutes at the top.
Romanian Deadlift Benefits
- Strengthens Posterior Chain: Targets hamstrings, glutes, and lower back for overall power.
- Improves Flexibility: Enhances hamstring flexibility through the eccentric motion.
- Enhances Athletic Performance: Builds strength and stability for sports and functional movements.
- Prevents Injuries: Strengthens the muscles that support proper hip and spine alignment.
- Promotes Muscle Balance: Complements quad-dominant exercises to develop symmetrical strength.
Romanian Deadlift Muscles Worked
The Romanian Deadlift primarily targets the hamstrings and glutes. The lower back muscles act as stabilizers, while the core and forearms support the movement.

Related Exercises
The One-Arm Kettlebell Swing is a dynamic exercise that targets the entire posterior chain, core, and shoulders. This functional movement helps in building strength, improving power, and enhancing grip endurance. By focusing on one side at a time, it challenges stability and coordination, making it a great addition to any workout routine. The exercise also aids in developing core strength and boosting cardiovascular endurance.
One-Arm Kettlebell Swing Video
How to Perform One-Arm Kettlebell Swings
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up Your Stance: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and place the kettlebell between your feet.
- Grip the Kettlebell: Bend at your hips and knees to grab the kettlebell with one hand, keeping your back straight.
- Engage Your Core: Brace your core and pull your shoulders back to maintain proper posture.
- Perform the Swing: Hinge at your hips and use the power from your glutes and hamstrings to swing the kettlebell forward to shoulder height. Keep your arm straight and avoid using your shoulder to lift the kettlebell.
- Control the Descent: Allow the kettlebell to swing back between your legs while maintaining control and repeating the movement.
- Alternate Sides: After completing your desired reps on one side, switch hands and repeat the movement on the other side.
One-Arm Kettlebell Swing Benefits
- Improved Power: This exercise builds explosive power in the hips and lower body, improving athletic performance.
- Enhanced Core Strength: The rotational stability required strengthens your core muscles effectively.
- Better Grip Strength: Holding the kettlebell with one hand challenges your grip and forearm strength.
- Increased Cardiovascular Fitness: The dynamic nature of the movement boosts heart rate, improving endurance.
- Improved Stability and Coordination: Focusing on one side at a time enhances balance and overall coordination.
One-Arm Kettlebell Swing Muscles Worked
The One-Arm Kettlebell Swing primarily targets the glutes, hamstrings, and core muscles. Secondary muscles include the lats, shoulders, and forearms, which work to stabilize and control the movement.

Related Exercises
The Front Squat (Clean Grip) is a highly effective lower body exercise that targets the quadriceps, glutes, and core. By using a clean grip, this variation of the front squat improves shoulder flexibility, core stability, and overall squat strength. This exercise is excellent for athletes and weightlifters aiming to build leg strength, improve posture, and increase performance in other lifts. The front squat (clean grip) is an essential movement in any strength training or athletic conditioning routine.
Front Squat (Clean Grip) Video
How to Perform Front Squats (Clean Grip)
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Set Up the Barbell: Start by placing the barbell on a squat rack at chest height. Position your hands in a clean grip (fingers wrapped around the bar and elbows high).
- Position the Bar: Step under the bar so that it rests on the front of your shoulders, keeping your elbows high and chest lifted.
- Grip the Bar: Ensure your hands are close together, with your fingers wrapped around the bar and your thumbs around it for a secure grip.
- Stand Tall: Take a deep breath, stand tall, and unrack the bar, stepping backward into your squat stance.
- Perform the Squat: Lower yourself into the squat by bending at the hips and knees, keeping your chest up and your back straight. Descend until your thighs are parallel to the ground or lower.
- Stand Back Up: Push through your heels to stand back up, extending your legs fully while maintaining a strong core throughout the movement.
Front Squat (Clean Grip) Benefits
- Improved Quad Strength: The front squat (clean grip) places more emphasis on the quadriceps compared to back squats, helping build stronger quads.
- Enhanced Core Stability: The clean grip position challenges your core to stabilize the torso throughout the movement, improving overall core strength.
- Better Posture: The upright position required during the squat helps improve posture by strengthening the muscles of the upper back and shoulders.
- Increased Flexibility: The clean grip position requires good wrist and shoulder flexibility, which improves your overall range of motion.
- Functional Strength: Front squats (clean grip) enhance functional strength, which can transfer to a variety of athletic movements.
Front Squat (Clean Grip) Muscles Worked
The Front Squat (Clean Grip) primarily targets the quadriceps, but also engages the glutes, hamstrings, lower back, and core. Additionally, the front rack position recruits the upper back, shoulders, and forearms to maintain stability during the movement.

Related Exercises
9.4
Excellent
Barbell Deadlift Images
Barbell Deadlift Instructions

- Approach the bar so that it is centered over your feet. Your feet should be about hip-width apart. Bend at the hip to grip the bar at shoulder-width allowing your shoulder blades to protract. Typically, you would use an alternating grip.
- With your feet and your grip set, take a big breath and then lower your hips and flex the knees until your shins contact the bar. Look forward with your head. Keep your chest up and your back arched, and begin driving through the heels to move the weight upward.
- After the bar passes the knees aggressively pull the bar back, pulling your shoulder blades together as you drive your hips forward into the bar.
- Lower the bar by bending at the hips and guiding it to the floor.
9.3
Excellent
Also known as Wide Stance Deadlift.
Sumo Deadlift Images
Sumo Deadlift Instructions

- Begin with a bar loaded on the ground. Approach the bar so that the bar intersects the middle of the feet. The feet should be set very wide, near the collars. Bend at the hips to grip the bar. The arms should be directly below the shoulders, inside the legs, and you can use a pronated grip, a mixed grip, or hook grip. Relax the shoulders, which in effect lengthens your arms.
- Take a breath, and then lower your hips, looking forward with your head with your chest up. Drive through the floor, spreading your feet apart, with your weight on the back half of your feet. Extend through the hips and knees.
- As the bar passes through the knees, lean back and drive the hips into the bar, pulling your shoulder blades together.
- Return the weight to the ground by bending at the hips and controlling the weight on the way down.





































